top of page

MIcrobial MEtabolite Signal Transduction
MIMEst (Ara's Lab)
Open position
MIME-st 연구실에서는 바이오인포매틱스 석·박사과정 및 박사후연구원을 모집합니다. 본 연구실은 Genetics, Epigenetics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics를 포함한 멀티오믹스 통합 분석으로 숙주 장내 환경 변화를 체계적으로 규명하고, Metagenomics 기반 분석을 통해 미생물–숙주 상호작용의 분자 기전을 연구합니다. 관심 있는 지원자는 CV를 첨부하여 ara.koh@postech.ac.kr로 연락해 주시기 바랍니다.
Research Interests
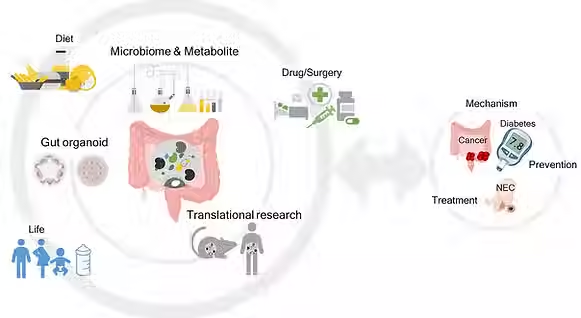
It is becoming evident that microbiota can directly signal to the host by generating bioactive metabolites, which would contribute to the development (i.e., imidazole propionate) or amelioration of metabolic diseases (i.e., short-chain fatty acids). In our lab, we aim to identify therapeutics for metabolic diseases including diabetes and cancer based on mechanistic understanding of the role of microbial metabolites. In addition, we will investigate inter-individual variations or failure in drug response in the context of microbial metabolite milieu by using organoids as a model system.
-
Mechanistic Understanding of the Impacts of Microbial Metabolites on Personalized Responses to Metabolic Intervention
-
Understanding the Impacts of Microbial Regulation of Small Intestine in Host Metabolism by Using Intestinal Organoid
-
Development of Personalized POST-Biotics based on Microbial Metabolites
Better and Safer Therapeutics for Human Diseases Based on Mechanistic Understanding of the Role of Microbial Metabolites
Selected Publications




Microbial Imidazole propionate Affects Responses to Metformin through p38g-Dependent Inhibitory AMPK Phosphorylation
Cell Metabolism. 2020. 10.06
From Association to Causality: the Role of the Gut Microbiota and Its Functional Products on Host Metabolism
Molecular Cell. 2020. 05. 21
Microbially Produced Imidazole Propionate Impairs Insulin Signaling through mTORC1
Cell. 2018.11.01
From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites
Cell. 2016. 06. 02
bottom of page